Your cart is currently empty!
Demystifying “01768 Ross Tech Wiki”: A Comprehensive Guide to VAG Vehicle Diagnostics
The cryptic code “01768 Ross Tech Wiki” often pops up when dealing with issues in Volkswagen Audi Group (VAG) vehicles. This essentially points towards a treasure trove of information – the Ross-Tech Wiki – and a specific fault code, 01768. This article will act as your guide, breaking down this code, its implications, and how you can utilize the Ross-Tech Wiki for effective troubleshooting.
Understanding the Significance of Fault Code 01768
In the world of automotive diagnostics, fault codes are like breadcrumbs leading you to the root of a problem. The code 01768 specifically signifies an issue with the “Linear Oxygen (Lambda) Sensor B1 S1: Open Circuit.”
Let’s break this down:
- Linear Oxygen (Lambda) Sensor: This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the oxygen content in your exhaust gases. This information is vital for the Engine Control Unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal combustion and reduced emissions.
- B1 S1: This denotes the specific location of the faulty sensor. “B1” typically refers to Bank 1 of the engine (in vehicles with two cylinder banks), and “S1” indicates Sensor 1, which is usually positioned before the catalytic converter.
- Open Circuit: This indicates a break or disruption in the electrical circuit connected to the oxygen sensor. It could mean a damaged sensor, wiring harness issues, or a faulty connection.
Navigating the Ross-Tech Wiki for 01768
The Ross-Tech Wiki is an invaluable online resource for anyone dealing with VAG vehicles. It provides detailed information on fault codes, diagnostic procedures, and repair guides.
Here’s how to utilize it for code 01768:
- Access the Wiki: Visit the Ross-Tech website and navigate to their Wiki section.
- Search for the Code: Use the search bar to look up “01768.” You can also browse by vehicle model and year for a more specific search.
- Explore the Information: The Wiki page for 01768 will provide you with:
- A detailed description of the fault code.
- Possible causes of the issue.
- Suggested diagnostic steps.
- Potential solutions and repair procedures.
 Ross-Tech Wiki Screenshot
Ross-Tech Wiki Screenshot
Common Causes and Troubleshooting Tips for 01768
Several factors can trigger the 01768 fault code. Here are some of the most common culprits:
- Faulty Oxygen Sensor: A malfunctioning sensor is often the primary cause.
- Wiring Issues: Damaged, corroded, or disconnected wiring in the sensor circuit can lead to an open circuit.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks in the exhaust system before the oxygen sensor can affect its readings.
- ECU Problems: While less common, a faulty ECU can also be the root cause.
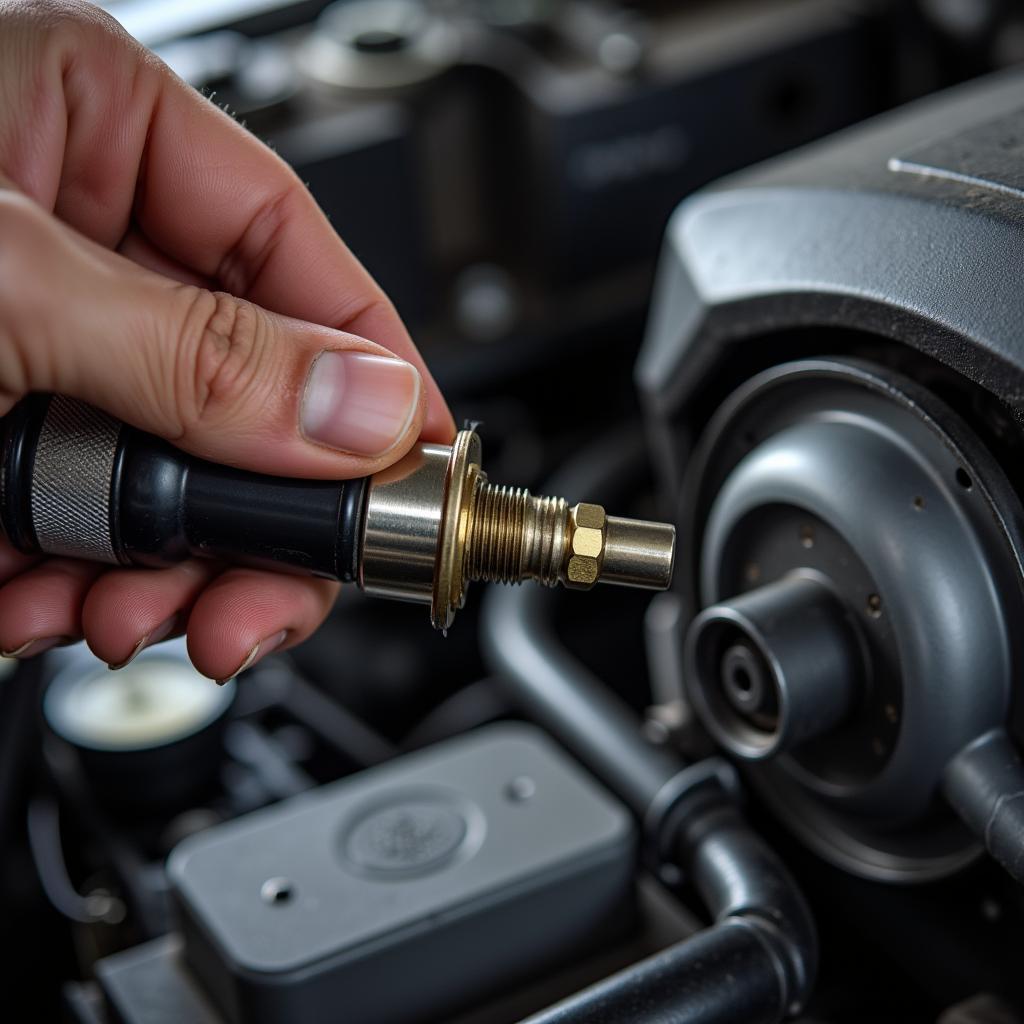 Inspecting an Oxygen Sensor
Inspecting an Oxygen Sensor
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the oxygen sensor and its wiring harness for any visible damage.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Look for signs of exhaust leaks around the sensor and the surrounding exhaust components.
- Wiring Continuity Test: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of the sensor wiring harness to ensure there are no breaks or shorts.
- Sensor Voltage Test: With the engine running, use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s voltage output to determine if it’s within the expected range.
Expert Insight:
“Always refer to the specific repair manual for your vehicle model and year, as procedures may vary,” advises John Miller, a veteran automotive electrician. “If you are uncomfortable working on your vehicle, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.”
Conclusion: 01768 Ross Tech Wiki – Your Go-To Resource
Encountering the 01768 fault code in your VAG vehicle can be concerning, but armed with the information from the Ross-Tech Wiki, you can confidently approach the issue. Remember, accurate diagnosis is key to effective repair.
Should you require professional assistance, don’t hesitate to contact us at VCDSTool at +1 (641) 206-8880 and our email address: vcdstool@gmail.com or visit our office located at 6719 W 70th Ave, Arvada, CO 80003, USA.
FAQs
1. Can I drive my car with the 01768 code?
It’s not advisable to drive for extended periods with this code as it might lead to reduced fuel economy, increased emissions, and potential engine performance issues.
2. How much does it cost to replace an oxygen sensor?
The cost can vary depending on the make and model of your vehicle and labor charges.
3. Can I replace the oxygen sensor myself?
While it’s possible, it requires some mechanical skill. If you’re unsure, consult a professional.
4. What happens if I ignore the 01768 code?
Ignoring the code could lead to catalytic converter damage, further engine issues, and failed emissions tests.
5. How often should oxygen sensors be replaced?
Oxygen sensors have a lifespan and are typically recommended for replacement between 60,000 to 90,000 miles.
by
Tags:
Leave a Reply