Your cart is currently empty!

Decoding the VW Under Turbo Fault Code
Understanding and addressing a “VW under turbo fault code” can be challenging. This article provides comprehensive guidance for VW owners, repair shops, and technicians to diagnose and resolve these issues effectively, covering common causes, diagnostic steps, and potential solutions.
 VW Under Turbo Fault Code Diagnostic Tools
VW Under Turbo Fault Code Diagnostic Tools
“Under turbo” fault codes generally indicate that the turbocharger isn’t producing the expected boost pressure. This could be due to various reasons, from simple issues like a vacuum leak to more complex problems like a faulty turbocharger or wastegate. Identifying the root cause is crucial for effective repair.
Understanding VW Under Turbo Fault Codes
VW vehicles utilize sophisticated engine management systems that monitor various parameters, including boost pressure. When the system detects that the boost pressure is below the expected range, it generates an “under boost” fault code. These codes can vary depending on the specific VW model and engine, but they typically point to a problem within the turbocharger system. For example, you might encounter codes like P0299 which is common in some Passat models. You can find more information about this specific code at p0299 code vw passat.
Common Causes of Under Turbo Fault Codes
Several factors can contribute to under boost conditions in VW vehicles. Some of the most common causes include:
- Vacuum Leaks: Leaks in the intake system can disrupt the pressure balance and reduce boost.
- Boost Leaks: Leaks in the charge air pipes or intercooler can also cause a loss of boost pressure.
- Faulty N75 Valve: The N75 valve controls the turbocharger’s wastegate. A malfunctioning valve can prevent the turbo from building sufficient boost.
- Clogged or Damaged Catalytic Converter: A restricted catalytic converter can create back pressure, affecting the turbo’s performance.
- Faulty Turbocharger: Internal damage to the turbocharger itself, such as worn bearings or damaged vanes, can reduce its efficiency.
- Sensor Issues: Malfunctioning sensors, such as the boost pressure sensor or the mass airflow sensor (MAF), can provide inaccurate readings to the engine control unit (ECU), leading to incorrect boost control.
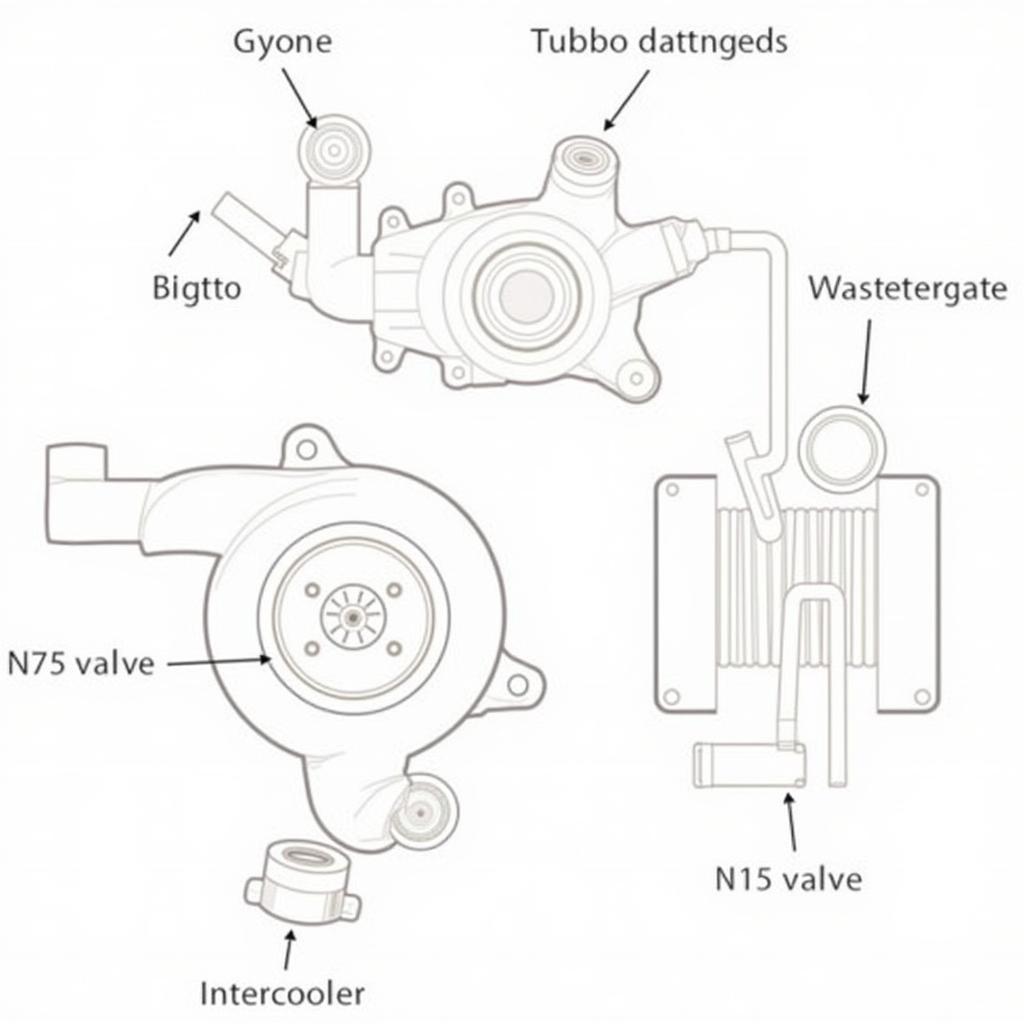 VW Turbocharger Components
VW Turbocharger Components
For those dealing with older models, knowing the right engine codes can be crucial. Check out resources like 2012 vw passat engine codes for specific information.
Diagnosing VW Under Turbo Fault Codes
Diagnosing an under boost condition requires a systematic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Retrieve Fault Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve any stored fault codes. Note down all codes and their descriptions.
- Inspect for Vacuum Leaks: Carefully examine all vacuum hoses and connections for cracks, splits, or loose fittings.
- Check for Boost Leaks: Inspect the charge air pipes, intercooler, and related connections for leaks. A boost leak tester can be helpful in identifying small leaks.
- Test the N75 Valve: Check the N75 valve’s operation using a vacuum pump and a multimeter.
- Inspect the Catalytic Converter: Check for restrictions in the catalytic converter. This might involve checking exhaust back pressure.
- Assess the Turbocharger: Inspect the turbocharger for any signs of damage or wear. Check for shaft play and listen for unusual noises.
“A thorough inspection is vital. Don’t just replace parts based on assumptions. Proper diagnostics saves time and money,” advises John Peterson, a seasoned automotive technician with over 20 years of experience.
Resolving VW Under Turbo Fault Codes
Once the cause of the under boost condition has been identified, appropriate repairs can be carried out. This may involve:
- Repairing Vacuum Leaks: Replace any damaged or loose vacuum hoses and fittings.
- Repairing Boost Leaks: Replace any damaged or leaky components in the charge air system.
- Replacing the N75 Valve: Install a new N75 valve if the old one is faulty.
- Replacing the Catalytic Converter: Replace a clogged or damaged catalytic converter.
- Replacing or Rebuilding the Turbocharger: If the turbocharger is damaged, it may need to be replaced or rebuilt.
- Repairing or Replacing Sensors: Replace any faulty sensors.
It’s always helpful to cross-reference information for TDI models, especially regarding specific fault codes. Resources like vw tdi fault code 17965 can be invaluable. Additionally, po237 vw fault code offers specific guidance on that particular code.
Conclusion
Addressing a “VW under turbo fault code” effectively requires understanding the system, performing thorough diagnostics, and implementing appropriate repairs. This article has provided valuable insights and practical guidance for VW owners, repair shops, and technicians to tackle these challenges. For further assistance, feel free to contact us at VCDSTool at +1 (641) 206-8880 and our email address: vcdstool@gmail.com or visit our office at 6719 W 70th Ave, Arvada, CO 80003, USA. We’re here to help you keep your VW running smoothly. For those interested in other VW model engine codes, resources such as 2015 vw passat tdi engine code are available.
by
Tags:
Leave a Reply