Your cart is currently empty!

Performing an Oxygen Sensor Test with VCDS: A Comprehensive Guide
Oxygen sensors play a crucial role in your vehicle’s engine performance and emissions control. They measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gases and relay this information to the engine control unit (ECU). This data enables the ECU to adjust the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal combustion and reduced emissions. When oxygen sensors malfunction, you might experience reduced fuel efficiency, rough idling, and even engine damage.
One of the most effective ways to diagnose oxygen sensor issues is by using a VCDS (VAG-COM Diagnostic System). This powerful diagnostic tool allows you to access the ECU, read error codes, and even perform live data analysis of your vehicle’s sensors, including the oxygen sensors.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps of performing an oxygen sensor test using VCDS, empowering you to diagnose and address oxygen sensor problems with confidence.
 VCDS Oxygen Sensor Test
VCDS Oxygen Sensor Test
Understanding Oxygen Sensors and their Importance
Before delving into the testing procedure, it’s crucial to understand the different types of oxygen sensors and their function. Most modern vehicles are equipped with two types of oxygen sensors:
-
Upstream Oxygen Sensor (Sensor 1): Located before the catalytic converter, this sensor primarily measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases to help the ECU regulate the air-fuel mixture.
-
Downstream Oxygen Sensor (Sensor 2): Positioned after the catalytic converter, this sensor monitors the efficiency of the catalytic converter by comparing its oxygen readings with the upstream sensor.
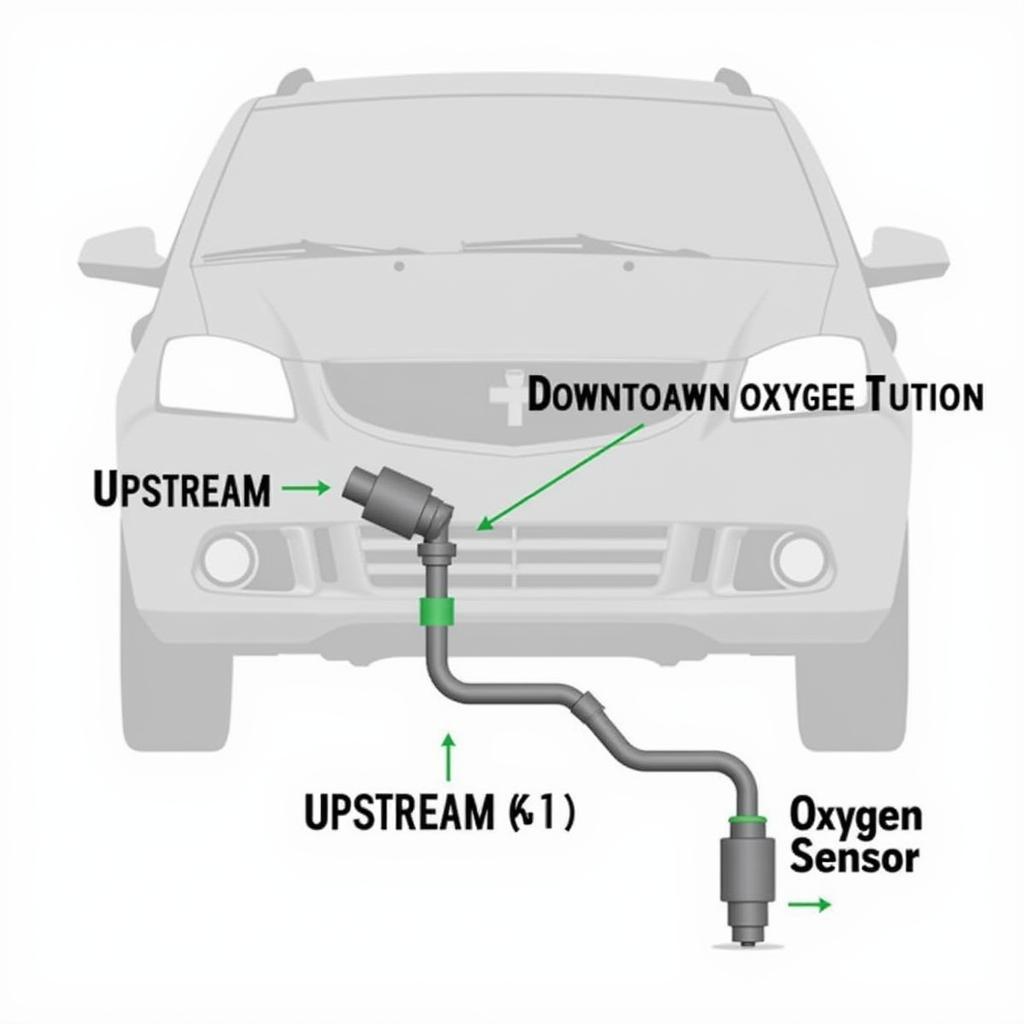 Upstream and Downstream Oxygen Sensors
Upstream and Downstream Oxygen Sensors
When to Suspect an Oxygen Sensor Issue
Several symptoms might indicate a failing oxygen sensor, prompting the need for a VCDS test:
- Check Engine Light Illumination: The most obvious sign, often accompanied by a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) related to oxygen sensors.
- Poor Fuel Economy: A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can disrupt the air-fuel ratio, leading to increased fuel consumption.
- Rough Idling or Engine Misfires: Inaccurate oxygen readings can result in an imbalanced air-fuel mixture, causing rough idling and engine performance issues.
- Increased Emissions: A faulty oxygen sensor can hinder the catalytic converter’s effectiveness, leading to increased harmful emissions.
Preparing for a VCDS Oxygen Sensor Test
Before initiating the test, ensure you have the following:
-
VCDS System: A genuine Ross-Tech VCDS interface and software are essential for this procedure.
-
Laptop with VCDS Software: Install the latest version of the VCDS software on your laptop for optimal compatibility and functionality.
-
OBD-II Cable: This cable connects your laptop’s VCDS software to your vehicle’s OBD-II port.
[elm327 vcds]
- Vehicle Information: Have your vehicle’s make, model, and engine code readily available, as you’ll need this information to access the correct ECU settings in VCDS.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing a VCDS Oxygen Sensor Test
Follow these steps meticulously to perform an accurate VCDS oxygen sensor test:
-
Connect the VCDS System: Connect the VCDS interface to your laptop’s USB port and the other end to your vehicle’s OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
-
Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition key to the “on” position without starting the engine. This will power up the ECU and allow communication with the VCDS system.
-
Launch VCDS Software: Open the VCDS software on your laptop and select the correct communication port and vehicle model.
 VCDS Software Interface
VCDS Software Interface
-
Access Engine Control Module: From the main menu, navigate to “Select Control Module” and choose “Engine” or the equivalent option for your specific vehicle model.
-
Go to Measuring Blocks (08): In the Engine control module, select “Measuring Blocks – 08.” This section displays live data from various engine sensors.
-
Identify Oxygen Sensor Groups: Scroll through the available measuring block groups to locate the groups that display oxygen sensor data. The specific group numbers might vary depending on your vehicle model, but common labels include “Oxygen Sensor Bank 1 Sensor 1,” “Oxygen Sensor Bank 2 Sensor 2,” etc.
-
Monitor Oxygen Sensor Readings: Observe the live data readings for each oxygen sensor. Pay close attention to the following:
-
Voltage Fluctuations: A healthy upstream oxygen sensor should rapidly fluctuate between 0.1 volts (lean) and 0.9 volts (rich) while the engine is running.
-
Downstream Sensor Stability: The downstream oxygen sensor should show a relatively stable voltage reading, indicating proper catalytic converter function.
-
Response Time: Observe how quickly the oxygen sensors respond to changes in engine speed or load. Slow response times could indicate sensor degradation.
-
[vcds mobile with bluetooth obd2]
-
Interpreting the Results: Analyze the oxygen sensor readings for any abnormalities. If you notice any of the following, it might signal a problem with the corresponding sensor:
- Stuck Voltage: An upstream sensor stuck at a specific voltage (e.g., 0.45V) suggests a faulty sensor.
- Slow Response: If a sensor takes too long to react to changes in engine conditions, it might be nearing the end of its lifespan.
- Inconsistent Readings: Erratic or inconsistent voltage readings from either sensor can indicate a problem.
-
Record and Analyze Error Codes: While in the Engine control module, navigate to the “Fault Codes – 02” section. This will display any stored fault codes related to engine performance, including those related to oxygen sensors. Record these codes and research their meanings to gain further insight into potential issues.
-
Consult a Professional if Needed: If you’re uncertain about interpreting the VCDS test results or suspect a faulty oxygen sensor, it’s always recommended to consult a qualified automotive electrician or mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
Conclusion
Performing a VCDS oxygen sensor test empowers you with the ability to diagnose and potentially resolve oxygen sensor-related issues. By following this comprehensive guide, you can gain valuable insights into your vehicle’s engine performance and ensure optimal fuel efficiency and emissions control.
Remember, while this guide provides valuable information, it’s not a substitute for professional expertise. If you encounter persistent issues or require assistance with repairs, don’t hesitate to contact the experts at +1 (641) 206-8880 and our email address: vcdstool@gmail.com or visit our office at 6719 W 70th Ave, Arvada, CO 80003, USA. Our team at vcdstool.com is always ready to provide expert guidance and support for all your automotive diagnostic needs.
by
Tags:
Leave a Reply