Modern vehicles are incredibly complex machines, relying heavily on sophisticated electronics to control everything from engine performance to safety systems. At the heart of this electronic network lies the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus, a critical communication system that allows various components within your car to talk to each other. When something goes wrong, or when you need to understand your vehicle’s health, a Can Bus Obdii Scan Tool becomes an indispensable piece of equipment.
The Need for Bus Systems in Modern Cars
Imagine the wiring nightmare if every sensor and actuator in your car required its own dedicated wire back to a central control unit. Early automobiles, with simpler electrical systems, could manage with point-to-point wiring. However, as cars evolved to incorporate more and more electronic features – engine management systems, anti-lock brakes, airbags, infotainment systems, and countless others – this approach became unsustainable. The sheer number of wires would add excessive weight, cost, and complexity, increasing the risk of failures and making diagnostics a mechanic’s worst nightmare.
This is where bus systems come into play. Think of a bus system as a shared communication highway for electronic signals. Instead of each component having a direct line, they all connect to this shared bus. This drastically reduces the amount of wiring needed, making the vehicle lighter, more cost-effective, and easier to manage.
To illustrate this, consider a simple example of controlling car lamps. Without a bus system, each lamp would require a dedicated wire:
- Headlamp: Wire 1 for on/off
- Taillight: Wire 2 for on/off
- Brake Light: Wire 3 for on/off
- Turn Signal (Left): Wire 4 for on/off
- Turn Signal (Right): Wire 5 for on/off
And so on. With a bus system, you could potentially control all these lamps using just a few wires. A simplified bus example might work like this: Imagine two wires. One wire acts as a selector, identifying which lamp you want to control, and the second wire acts as a switch, turning it on or off. While real-world bus systems are far more sophisticated, this illustrates the fundamental principle of transmitting more information with fewer wires.
CAN Bus: The Backbone of Automotive Communication
Among the various types of bus systems used in vehicles, the CAN bus stands out as the most prevalent and crucial. Developed by Bosch in the 1980s for automotive applications, CAN is designed to be robust, reliable, and efficient for real-time control and data communication. It allows microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other in applications without a host computer.
In a car, the CAN bus network connects critical components like the Engine Control Unit (ECU), Transmission Control Unit (TCU), Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), Airbag Control Unit, and many more. This network enables these systems to share data and coordinate their actions. For instance, the ABS system needs to know the wheel speed from sensors, which are also used by the ECU for traction control and other functions. Instead of each system having its own wheel speed sensors and wiring, they can all access this data through the CAN bus.
OBD-II: Diagnostics Through the CAN Bus
Now, where does OBD-II fit into all of this? On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) is a standardized system that provides access to vehicle diagnostic information. It’s essentially a set of protocols and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that allow mechanics and car owners to understand the health and status of a vehicle’s systems.
Think of OBD-II as a language spoken to understand your car’s condition, and CAN bus as one of the communication channels (like a telephone line) used to transmit this language. OBD-II doesn’t dictate the physical communication method; it specifies the content and format of the diagnostic information. While OBD-II can operate over various physical layers, including CAN bus, it also supports other communication protocols. However, CAN bus has become the dominant physical layer for OBD-II in modern vehicles, especially in markets like the US and Europe.
CAN Bus OBDII Scan Tools: Your Diagnostic Window
A CAN bus OBDII scan tool is a device designed to communicate with your vehicle’s computer system through the OBD-II port, utilizing the CAN bus protocol. This tool allows you to “speak” the OBD-II language and retrieve valuable diagnostic data. These tools range from basic code readers that display generic fault codes to advanced professional-grade scanners capable of in-depth system analysis, live data streaming, and even bi-directional control (sending commands to the vehicle).
To use a CAN bus OBDII scan tool, you simply locate the OBD-II port in your vehicle – typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side – and plug in the scanner. Once connected, the scan tool can:
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): These codes are set by the vehicle’s computer when it detects a problem in a system. The scan tool displays these codes, giving you a starting point for diagnosis.
- Clear DTCs: After a fault is repaired, you can use the scan tool to clear the DTCs and turn off the check engine light (or other warning lights).
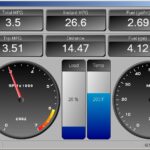
- View Live Data: Scan tools can display real-time data from various sensors and systems, such as engine speed (RPM), coolant temperature, oxygen sensor readings, and much more. This live data is invaluable for diagnosing intermittent problems and understanding how your vehicle is performing.
- Perform Actuator Tests: More advanced scan tools can perform actuator tests, allowing you to command certain components (like relays, solenoids, or motors) to activate and verify their functionality.
Conclusion: Empowering Vehicle Diagnostics
In conclusion, CAN bus OBDII scan tools are essential tools for anyone involved in modern vehicle maintenance and repair, from professional technicians to DIY car enthusiasts. They provide a window into the complex electronic systems of today’s cars, allowing for efficient and accurate diagnostics. By understanding the fundamentals of bus systems, CAN bus, and OBD-II, and utilizing a CAN bus OBDII scan tool, you can take a proactive approach to vehicle maintenance, troubleshoot issues effectively, and ensure your car remains in optimal running condition.