If you’re in charge of a fleet of vehicles, from sturdy pickup trucks to agile light-duty vans, you’ve probably encountered the cryptic world of “OBD-II codes.” But don’t let the technical jargon intimidate you. Think of OBD-II codes as your vehicles’ way of communicating, sending messages about their internal health directly to you. For fleet managers and vehicle owners alike, understanding these codes is crucial for proactive vehicle maintenance and ensuring smooth operations.
This guide will demystify OBD-II codes, explaining what they are, how they function, and why they are indispensable for managing your fleet effectively. We’ll also explore how to leverage car scan tools to interpret and manage these codes, regardless of your fleet’s size.
What Exactly Are Car Scan Tool Codes (OBD-II Codes)?
Onboard diagnostics (OBD-II codes), often accessed via car scan tools, are essentially alphanumeric codes generated by your vehicle’s onboard computer system. These codes are the vehicle’s way of signaling detected issues within its various systems. Imagine them as digital alerts from your vehicle’s internal monitoring system.
Various components within your vehicle, including the engine, transmission, and emission control systems, constantly communicate with the central onboard computer. When the computer detects an anomaly in your vehicle’s operation, it generates a specific diagnostic trouble code (DTC). This is where a car scan tool becomes invaluable. By connecting a scan tool to your vehicle’s OBD-II port, usually found under the dashboard, you can retrieve these numerical codes.
These codes act as pointers, directing you or your mechanic towards the root of the problem. They can range from indicating minor glitches to signaling potentially serious malfunctions. For instance, the universally recognized “Check Engine” light illuminates when the computer detects that a system or component within the engine isn’t performing as expected. A car scan tool then translates this light into a specific code, providing a crucial first step in troubleshooting and informed decision-making for your fleet operations.
Navigating the Different Types of Car Scan Tool Codes
When a car scan tool reveals an OBD-II code from one of your fleet vehicles, understanding the code’s category is the first step towards effective diagnosis. OBD-II codes are broadly categorized into four main types, each relating to a different area of the vehicle. Familiarity with these categories will streamline your diagnostic process and ensure efficient issue resolution.
Powertrain Codes: Engine and Transmission Issues
Powertrain codes, a common category revealed by car scan tools, signal problems within the vehicle’s engine, transmission, and drivetrain. These codes are critical as they point to issues affecting the vehicle’s power source and overall performance.
For example, the powertrain code P0101 indicates a potential issue with the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor. The MAF sensor is vital for measuring the amount of air entering the engine, enabling the vehicle’s computer to calculate the optimal air-fuel mixture for peak performance. A malfunctioning MAF sensor, flagged by a car scan tool with this code, can lead to reduced fuel efficiency and compromised engine performance. Addressing this promptly ensures your fleet vehicles maintain optimal fuel consumption and power.
Body Codes: Addressing Comfort and Safety Systems
Body codes, another category identified by car scan tools, pinpoint potential problems within the vehicle’s body systems. This includes systems that contribute to comfort and safety, such as lighting, airbag systems, and climate control.
For instance, a body code B0020 indicates a problem with the driver’s side airbag deployment circuit. This is a critical safety concern. If a car scan tool reveals this code, it means that in a collision, the driver’s side airbag might not deploy correctly. Airbags are crucial safety features, and addressing body codes promptly ensures the safety of your drivers.
Chassis Codes: Suspension, Steering, and Braking Concerns
Chassis codes, when detected by a car scan tool, highlight potential issues within the vehicle’s chassis and related systems. This category encompasses crucial systems like the suspension, steering, and brakes, all of which are vital for vehicle control and safety.
Consider the chassis code C1234, which signifies a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor. A malfunctioning wheel speed sensor, detected by a car scan tool, can have serious consequences. It can destabilize the vehicle’s handling, making driving unsafe, particularly in adverse conditions. Furthermore, it can impact the anti-lock braking system (ABS), reducing braking effectiveness. Addressing chassis codes is paramount for maintaining vehicle stability and braking performance.
Network Communication Codes: Issues in Vehicle Communication
Network communication codes, identified by car scan tools, signal potential problems within the vehicle’s internal communication network. This network involves modules and sensors that constantly exchange information to ensure all systems work in harmony.
Take, for example, the network communication code U0100, indicating a loss of communication with the Engine Control Module (ECM). Often, this issue can be traced back to a failing battery. If a car scan tool displays the U0100 code, you might observe symptoms like reduced engine power, sluggish acceleration, and decreased fuel economy. In severe cases, this communication breakdown could even lead to engine stalling while driving, presenting a significant safety hazard. Network communication codes highlight the interconnectedness of vehicle systems and the importance of a healthy electrical system.
Decoding Car Scan Tool Codes: Understanding the Structure
Car Scan Tool Codes are structured in a standardized five-character format, consisting of letters and numbers. Each position within the code provides specific information, acting as a roadmap to the problem.
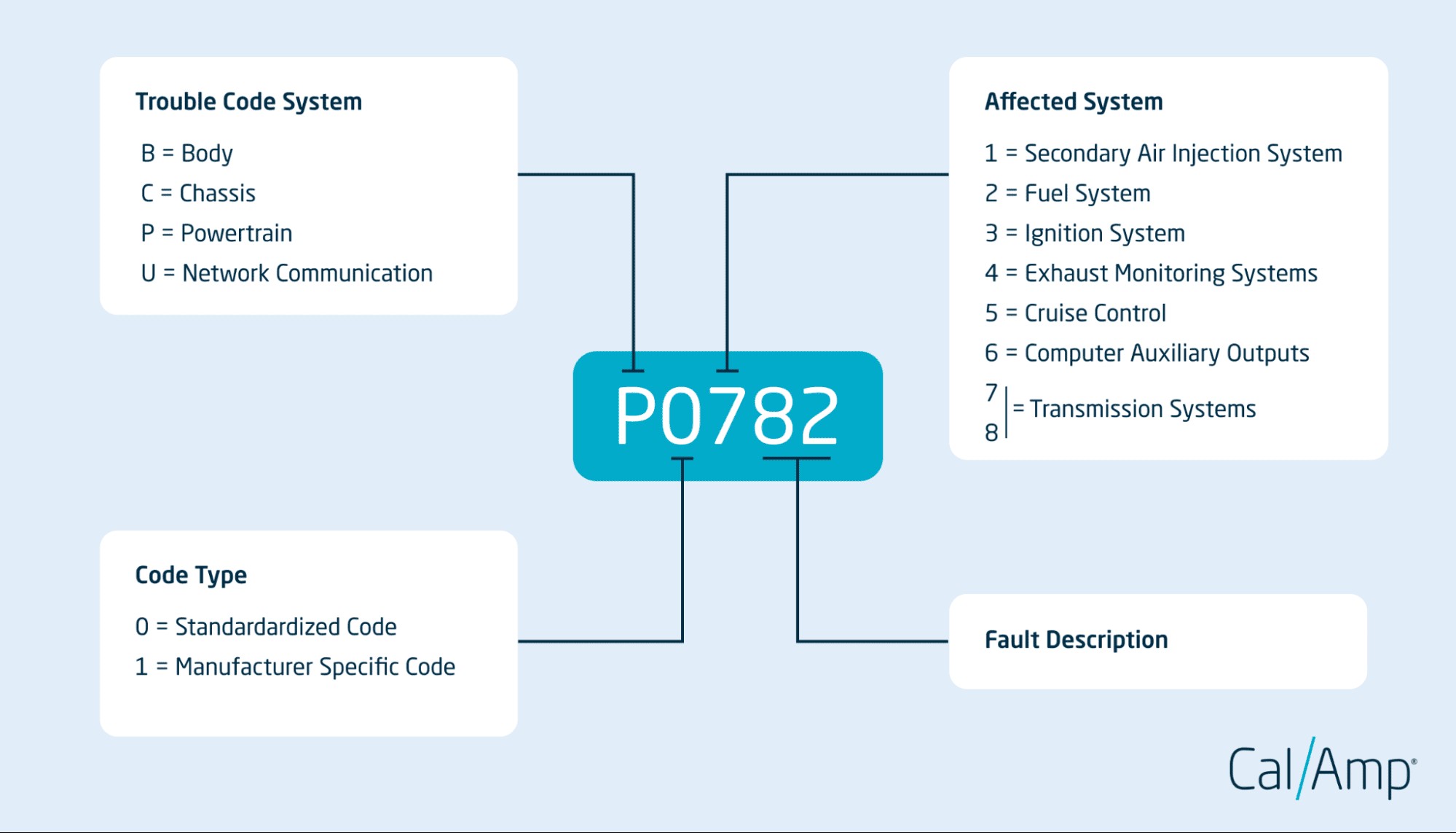 What OBD2 codes mean
What OBD2 codes mean
Understanding this structure – including the trouble code system, code type, affected system, and specific code – is key to effectively using car scan tool outputs for accurate diagnosis.
Trouble Code System: Identifying the Area of Concern
The first character of a car scan tool code is always a letter, indicating the primary system affected. This letter categorizes the problem area:
- P (Powertrain): Relates to the engine, transmission, and related drivetrain components.
- C (Chassis): Indicates issues with chassis systems like brakes, steering, and suspension.
- B (Body): Points to problems within the vehicle’s body systems, such as airbags, lights, and comfort features.
- U (Network Communication): Signifies communication issues within the vehicle’s computer network.
Code Type: Standardized vs. Manufacturer-Specific
The second character of a car scan tool code is a number, specifying the code type:
- 0 (Standardized Code): These are generic codes, common across all vehicle makes and models. For example, ‘P0420’ universally suggests a catalytic converter issue.
- 1 (Manufacturer-Specific Code): These codes are unique to specific automakers and offer more granular detail about the problem. For instance, ‘P1101’ might be a manufacturer-specific code related to the air intake system in a particular vehicle brand.
Affected System: Pinpointing the Subsystem
The third character is a number that further specifies the affected subsystem within the broader category (Powertrain, Chassis, Body, or Network Communication). While the exact meaning of these numbers can be detailed, some common affected systems include:
- 1: Secondary Air Injection System: Related to emissions reduction.
- 2: Fuel System: Issues with fuel delivery, mixture, or emissions from the fuel system.
- 3: Ignition System: Problems with spark plugs, coils, or other ignition components.
- 4: Exhaust Monitoring Systems: Issues with oxygen sensors, catalytic converters, and other emission control components.
- 5: Cruise Control System: Malfunctions within the cruise control system.
- 6: Computer Auxiliary Outputs: Problems with computer-controlled accessories like lights or fans.
- 7 & 8: Transmission System: Issues within the automatic or manual transmission.
Specific Code: The Precise Problem
The final two characters of a car scan tool code are numbers that provide a highly specific identifier of the problem. For example, in the code “P0420,” the “20” pinpoints the catalytic converter as the likely source of the powertrain issue. These specific codes often require reference to a code database for precise interpretation.
Clearing Car Scan Tool Codes: When and How
While clearing car scan tool codes might seem like a quick fix, it’s generally not recommended without addressing the underlying issue. However, there are situations where codes might need clearing, particularly after repairs or for diagnostic purposes. Here are three methods to clear OBD-II codes, keeping in mind that resolving the root problem is always the priority.
Using a Car Scan Tool to Clear Codes
Car scan tools are not just for reading codes; they are also essential for clearing them. After diagnosing and repairing the issue indicated by a DTC, a car scan tool can be used to clear the code and reset the “Check Engine” light. This confirms that the repair has been registered by the vehicle’s computer system.
Car scan tools are particularly useful for managing codes related to the fuel and emission systems. By clearing codes after addressing issues in these systems, you can ensure accurate monitoring of future problems and maintain optimal diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) management.
Drive Cycle: Allowing Codes to Clear Naturally
In some instances, certain car scan tool codes may clear themselves after a series of successful “drive cycles.” A drive cycle involves operating the vehicle under specific conditions (speed, temperature, duration) that allow the onboard computer to re-evaluate the system and clear the code if the issue is resolved.
While drive cycles can be effective for some codes, they are not a guaranteed solution for all problems. They are more suitable for intermittent or minor issues that the system can self-correct.
Professional Mechanic: For Comprehensive Diagnosis and Clearing
If you are uncertain about interpreting car scan tool codes, or if the “Check Engine” light reappears after clearing codes, consulting a professional mechanic is advisable. Mechanics possess the expertise, experience, and advanced diagnostic equipment to accurately pinpoint the root cause of OBD-II codes.
Mechanics can not only clear codes but also conduct thorough inspections to ensure the problem is properly fixed, not just temporarily masked. This approach prevents potential further damage and ensures long-term vehicle reliability, saving you money and potential breakdowns in the long run. Furthermore, professional mechanics can often identify related issues that might not be immediately apparent from the car scan tool code alone.
Preventing Car Scan Tool Codes: Proactive Vehicle Care
Preventing OBD-II codes from appearing in the first place is always the best approach, saving time, money, and potential vehicle downtime for your fleet.
[Picture #5] Let’s explore two key strategies for proactive vehicle maintenance that minimize the occurrence of car scan tool codes and keep your fleet running smoothly.
Regular Vehicle Maintenance: The Foundation of Prevention
Consistent and thorough vehicle maintenance, including routine inspections, fluid changes, and timely repairs, is the most effective way to prevent car scan tool codes. By addressing minor issues proactively, before they escalate, you significantly reduce the likelihood of triggering codes and ensure your vehicles operate efficiently and reliably.
- Routine Tasks: Essential maintenance includes regular oil changes, air filter replacements, spark plug checks, brake inspections, and tire rotations.
- Scheduled Timing: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, found in your vehicle’s owner’s manual. This schedule is designed to address maintenance needs based on mileage and time intervals.
- Professional Service: For comprehensive preventative maintenance, consider utilizing a trusted mechanic who can perform detailed inspections and address potential problems before they develop into issues that trigger car scan tool codes.
Quality Fuel and Fluids: Protecting Vehicle Systems
Using high-quality fuel and fluids is another critical preventative measure against car scan tool codes. Inferior fluids can lead to inadequate lubrication, increased wear and tear, and subsequent engine or transmission codes. Low-quality fuel can cause incomplete combustion, leading to performance issues and emissions-related codes, all of which can be detected by car scan tools.
- Fuel Choice: Consistently choose reputable gas stations and use fuel that meets or exceeds the vehicle’s recommended octane rating.
- Fluid Quality: Always use manufacturer-recommended fluids, including engine oil, transmission fluid, coolant, and brake fluid. These are formulated to meet specific vehicle requirements.
- Regular Fluid Checks: Periodically check and top off essential fluids, particularly engine oil, to ensure they are at the correct levels and maintaining their protective properties.
Streamlining Car Scan Tool Code Management for Fleets
For fleet managers, efficiently managing car scan tool codes across a fleet of vehicles is crucial. Standardizing processes and leveraging automation can significantly reduce the burden of individual vehicle inspections and code management.
Here are effective strategies for handling car scan tool codes in a fleet environment:
Centralized Code Tracking: A Unified System
Centralizing car scan tool code tracking involves consolidating diagnostic data from all fleet vehicles into a single, accessible system. This simplifies data management, allowing for easy access and analysis. Solutions like the CalAmp iOn enhance this by providing real-time insights into code occurrences, vehicle performance trends, and maintenance needs.
A centralized system offers real-time visibility, keeping fleet managers immediately informed of emerging issues. It also enables historical data analysis, helping identify recurring problems within specific vehicles or across vehicle types, facilitating proactive maintenance strategies.
Continuous Fleet Monitoring: Real-Time Diagnostics
Implementing continuous fleet monitoring utilizes telematics systems to gather real-time data from all fleet vehicles. This data includes vehicle location, performance metrics, and, importantly, car scan tool code occurrences.
With continuous monitoring, fleet managers can detect car scan tool codes and associated issues as soon as they arise. This enables rapid response, minimizing vehicle downtime and preventing minor problems from escalating into major, costly repairs. Proactive monitoring also contributes to cost savings through optimized vehicle performance and improved fuel efficiency.
Prioritized Repairs: Severity-Based Action
Fleet managers should implement a system for prioritizing repairs based on the severity of the car scan tool codes and their potential impact on vehicle operation. This ensures efficient allocation of maintenance resources.
High-severity codes, indicating critical issues that could lead to breakdowns or safety concerns, should be addressed immediately to minimize vehicle downtime and maintain uninterrupted fleet operations. Lower-severity codes can be scheduled for repair during routine maintenance windows, optimizing workflow and resource management.
In Conclusion: Car Scan Tools and Proactive Vehicle Management
Car scan tool codes are invaluable communication signals from your vehicles, indicating a range of potential issues from minor sensor glitches to significant transmission problems. Recognizing and acting upon these messages is essential for maintaining your fleet’s optimal condition.
While car scan tools are powerful for reading codes and diagnosing problems, comprehensive fleet management solutions like CalAmp offer even greater advantages. These systems not only read codes but also provide real-time insights into vehicle performance, location tracking, and proactive maintenance scheduling.
Request a demo today to discover how CalAmp iOn can revolutionize your fleet management strategy, providing complete visibility and control over your vehicle operations.
