Your cart is currently empty!
Decoding VCDS Code Default 01314: A Comprehensive Guide
The dreaded “Check Engine” light illuminates your dashboard, and a quick scan with your VCDS reveals the cryptic code: 01314. What does it mean, and more importantly, what do you do? This guide will decipher the mystery of VCDS code default 01314, equipping you with the knowledge to diagnose and fix the issue effectively, whether you’re a seasoned mechanic or a concerned car owner.
Understanding the Infamous 01314 Code
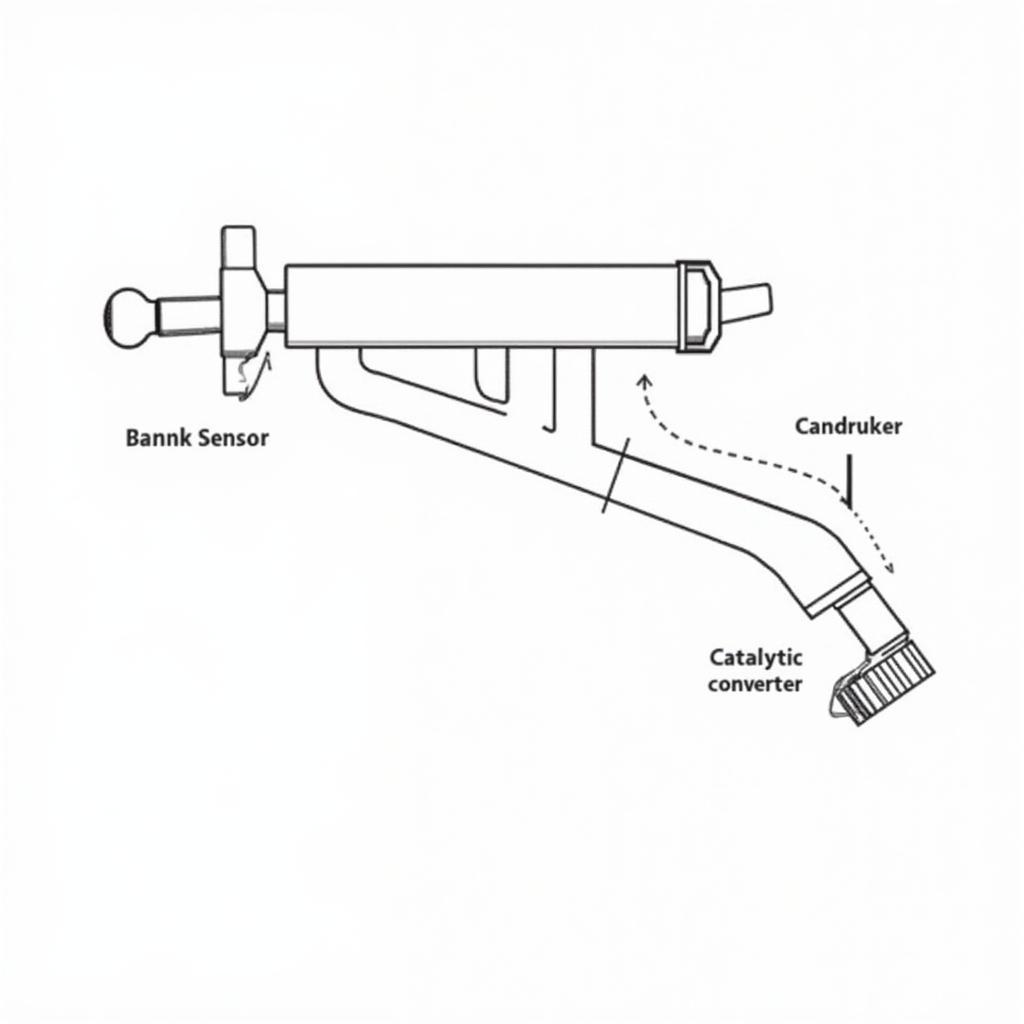
The 01314 code specifically points to an issue with the oxygen sensor (O2 sensor), also known as the lambda sensor, located downstream of the catalytic converter (Bank1-Sensor2). This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring the exhaust gases after they pass through the catalytic converter, ensuring efficient combustion and emission control. When this sensor malfunctions, it can lead to several problems, including reduced fuel economy, increased emissions, and even damage to the catalytic converter itself. But don’t panic! Understanding the underlying causes is the first step toward a solution.
 VCDS Code 01314 and O2 Sensor Location
VCDS Code 01314 and O2 Sensor Location
Common Causes of VCDS Code 01314
Several factors can trigger the 01314 code. The most common culprit is a faulty O2 sensor itself. Over time, the sensor can become contaminated or wear out, leading to inaccurate readings. However, other issues can mimic a faulty sensor, such as exhaust leaks, wiring problems, or even a failing catalytic converter.
- Faulty O2 Sensor: The sensor itself might be damaged or worn out due to age and exposure to high temperatures.
- Exhaust Leaks: Leaks before the sensor can introduce fresh air into the exhaust stream, disrupting the sensor’s readings.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring connecting the sensor to the engine control unit (ECU) can disrupt the signal transmission.
- Failing Catalytic Converter: While less common, a failing catalytic converter can also trigger the 01314 code.
Diagnosing and Fixing the 01314 Fault Code
Before replacing any parts, it’s essential to diagnose the problem accurately. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the wiring and connector for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Check for Exhaust Leaks: Inspect the exhaust system for any leaks, particularly before the downstream O2 sensor.
- VCDS Scan: Use your VCDS to monitor the sensor readings in real-time. This will help you determine if the sensor is responding correctly.
- Voltage Test: Use a multimeter to test the sensor’s voltage output. This can provide further insight into its functionality.
“A thorough diagnosis is key,” says automotive electrical expert, Dr. Robert Miller. “Replacing parts without proper diagnosis can lead to unnecessary expenses and may not resolve the underlying issue.”
What if it’s the Catalytic Converter?
While less frequent, a faulty catalytic converter can also trigger the 01314 code. If you suspect the converter is the problem, consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
 Catalytic Converter Inspection for VCDS 01314
Catalytic Converter Inspection for VCDS 01314
Preventing Future 01314 Codes
Regular maintenance can help prevent future occurrences of the 01314 code. Ensuring your engine is running correctly, using quality fuel, and addressing exhaust leaks promptly can prolong the life of your O2 sensors and catalytic converter.
“Preventive maintenance is always better than reactive repair,” adds Dr. Miller. “Regular checks and addressing minor issues promptly can save you significant time and money in the long run.”
Conclusion: Taking Control of VCDS Code Default 01314
Understanding VCDS code default 01314 empowers you to address the issue effectively. By following the diagnostic steps outlined in this guide, you can pinpoint the cause and implement the necessary repairs, keeping your car running smoothly and efficiently. For further assistance and expert diagnostics, connect with us at VCDStool at +1 (641) 206-8880 and our email address: vcdstool@gmail.com or visit our office at 6719 W 70th Ave, Arvada, CO 80003, USA.
 VCDS Diagnostic Tool Reading 01314 Code
VCDS Diagnostic Tool Reading 01314 Code
FAQ
- Can I drive my car with the 01314 code? While you can technically drive, it’s best to address the issue promptly to avoid further damage and potential performance issues.
- How much does it cost to replace an O2 sensor? The cost varies depending on the make and model of your car but generally ranges.
- Can I replace the O2 sensor myself? Yes, with basic mechanical skills and the right tools, you can replace it yourself.
- How often should I replace my O2 sensors? It depends on the car and driving conditions, but generally every 60,000 to 90,000 miles.
- What does “Bank1-Sensor2” mean? Bank 1 refers to the side of the engine with cylinder #1. Sensor 2 indicates the downstream sensor after the catalytic converter.
- Will clearing the code fix the problem? No, clearing the code only resets the check engine light. The underlying issue will persist.
- Can a bad fuel pump cause this code? While unlikely, a severely malfunctioning fuel pump can indirectly contribute to issues that trigger this code.
by
Tags:
Leave a Reply