Your cart is currently empty!
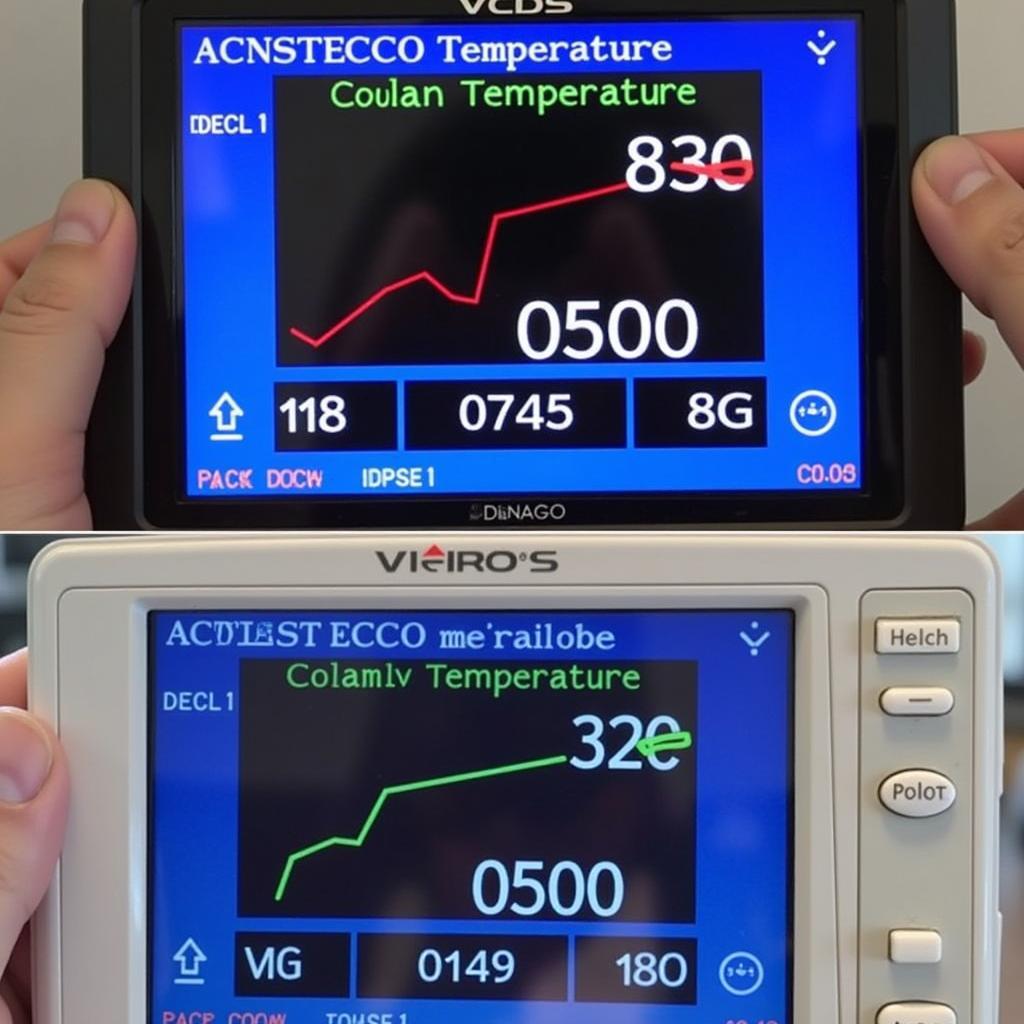
Understanding the VCDS Coolant Temp Measuring Block
The VCDS coolant temp measuring block is a critical component for diagnosing and troubleshooting cooling system issues in Volkswagen, Audi, Seat, and Skoda vehicles. This diagnostic tool allows you to access real-time data from the coolant temperature sensor, providing valuable insights into the overall health and performance of your vehicle’s cooling system. Accessing this data via VCDS (Vag-Com Diagnostic System) can help pinpoint problems like faulty thermostats, malfunctioning fans, or even potential head gasket issues.
Knowing how to interpret the readings from the vcds coolant temp measuring block is essential for any DIY mechanic or professional technician. This article will delve into the intricacies of this measuring block, providing you with the knowledge you need to diagnose and fix cooling system problems. You can find more information on using VCDS in the how to install and use vcds guide.
What is the VCDS Coolant Temp Measuring Block?
The VCDS coolant temp measuring block provides access to the raw data from your car’s coolant temperature sensor (CTS). This sensor, usually located near the thermostat or on the engine block, measures the coolant temperature and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU uses this data to adjust fuel injection, ignition timing, and fan operation. By using VCDS, you can monitor this data stream directly, gaining a detailed view of your cooling system’s operation.
Why is Monitoring Coolant Temperature Important?
Maintaining the correct coolant temperature is crucial for optimal engine performance and longevity. Overheating can lead to severe engine damage, including warped cylinder heads and cracked engine blocks. Conversely, a consistently low operating temperature can reduce fuel efficiency and increase emissions. Regularly monitoring your coolant temperature with the VCDS system allows you to proactively address potential issues before they escalate into costly repairs.
How to Access the Coolant Temp Measuring Block with VCDS
Accessing the vcds coolant temp measuring block is a straightforward process. First, connect your VCDS interface to your vehicle’s OBD2 port. Then, launch the VCDS software on your computer. Select the correct control module for your engine, usually labeled “Engine” or something similar. Navigate to the “Measuring Blocks” or “Data Blocks” section. Locate the measuring block associated with the coolant temperature. The specific block number may vary depending on your vehicle’s model and year. Refer to your vehicle’s specific repair manual or online resources like vcds obd2 for the correct measuring block number.
Interpreting the Data
Once you’ve accessed the measuring block, you’ll see a series of values. The most important value is the actual coolant temperature reading. Compare this value to the specified coolant temperature, which represents the ideal operating temperature for your engine. A significant discrepancy between these two values could indicate a problem.
 VCDS Coolant Temperature Comparison
VCDS Coolant Temperature Comparison
“Regular monitoring is key,” advises John Miller, a seasoned automotive technician with over 20 years of experience. “Using VCDS to check your coolant temp measuring block regularly can prevent minor issues from becoming major headaches.”
Troubleshooting Common Coolant Temperature Issues with VCDS
The VCDS system is a powerful tool for diagnosing a range of coolant temperature-related problems. Here are a few examples:
- Stuck Thermostat: If the coolant temperature remains consistently low, even after the engine has warmed up, it could indicate a stuck-open thermostat.
- Faulty Coolant Temperature Sensor: Inaccurate or erratic readings could point to a faulty CTS. You can compare the VCDS readings with a separate temperature gauge to confirm this diagnosis.
- Cooling Fan Malfunction: If the coolant temperature rises excessively, especially during idling or low-speed driving, it could suggest a problem with the cooling fan.
- Potential Head Gasket Issues: In severe cases, a blown head gasket can lead to coolant leaks and overheating. While VCDS can’t definitively diagnose a head gasket issue, it can provide valuable data to support further investigation. For further information on vehicle diagnostics, resources like hex net wifi vcds can be helpful.
Using VCDS for Preventative Maintenance
Regularly checking your vcds coolant temp measuring block isn’t just for troubleshooting problems; it’s also a valuable preventative maintenance practice. By monitoring your coolant temperature, you can identify potential issues early on, preventing them from escalating into major repairs.
“Think of it like taking your car’s pulse,” says Sarah Chen, an automotive engineer specializing in diagnostics. “VCDS gives you that insight, allowing you to catch problems before they become critical.”
Conclusion
The vcds coolant temp measuring block is a crucial tool for understanding and maintaining your vehicle’s cooling system. By learning how to access and interpret the data, you can diagnose and troubleshoot a wide range of cooling system issues, saving yourself time and money in the long run. You can even use tools such as vcds logfahrt 1.8 t for more specialized diagnostics. For further assistance or support, connect with us at vcdstool, +1 (641) 206-8880 and our email address: vcdstool@gmail.com or visit our office at 6719 W 70th Ave, Arvada, CO 80003, USA.
by
Tags:
Leave a Reply