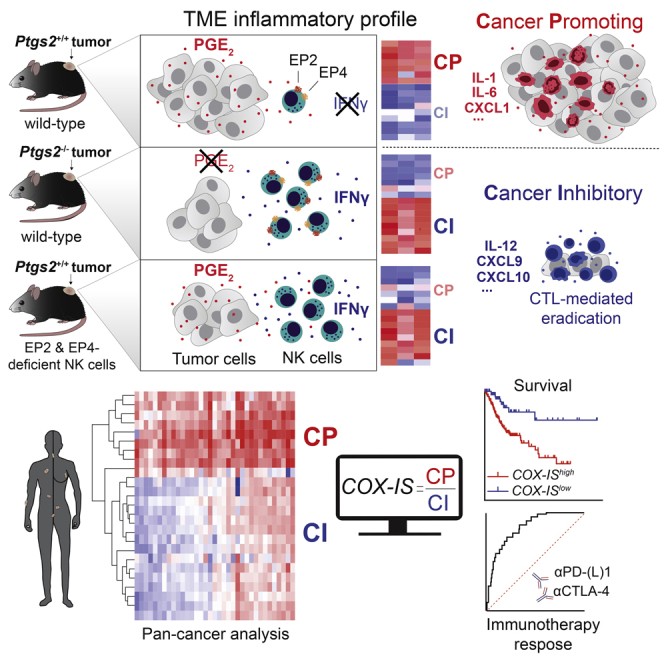
Inflammation plays a dual role in cancer, either promoting or hindering its progression and response to therapy. Researchers have developed a novel approach, leveraging the Bonavita Scan Tool, to analyze tumor inflammation and predict immunotherapy success. This tool, derived from extensive murine studies and validated across human cancer datasets, offers a promising strategy for personalized cancer treatment.
Deciphering the Inflammatory Tumor Microenvironment with the Bonavita Scan Tool
The Bonavita scan tool focuses on the intricate interplay between the tumor microenvironment (TME) and the immune system. Specifically, it identifies key inflammatory factors and immune cell populations associated with either tumor suppression or progression. This analysis provides crucial insights into predicting patient survival and response to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB).
NK Cells: Key Players in Tumor Control
The Bonavita scan tool highlights the critical role of Natural Killer (NK) cells in orchestrating anti-tumor immune responses. In murine models, early infiltration of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)-producing NK cells into the tumor was found to trigger a significant shift in the TME, ultimately leading to cytotoxic T cell (CTL)-mediated tumor eradication.
PGE2: A Suppressor of Anti-tumor Immunity
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), a molecule produced by tumor cells, was identified as a key suppressor of anti-tumor immunity. PGE2 acts on specific receptors (EP2 and EP4) on NK cells, hindering their ability to remodel the TME and enabling immune evasion. The Bonavita scan tool assesses the levels of PGE2 and its receptors, providing valuable information about the tumor’s ability to escape immune surveillance.
COX-2: A Marker of Cancer-Promoting Inflammation
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme involved in PGE2 synthesis, is a central component of the Bonavita scan tool analysis. High COX-2 expression is associated with a cancer-promoting inflammatory environment, characterized by increased levels of molecules that support tumor growth and suppress immune responses.
The COX-2-Associated Inflammatory Signature (COX-IS)
The Bonavita scan tool utilizes a gene expression signature, called the COX-IS, which integrates the expression levels of both cancer-promoting and cancer-inhibitory inflammatory factors. This signature provides a comprehensive assessment of the tumor’s inflammatory state and has demonstrated strong prognostic value across multiple human cancers.
Predicting Immunotherapy Response with the COX-IS
The COX-IS has shown remarkable accuracy in predicting patient response to ICB therapy. In various clinical trials, patients with a lower COX-IS exhibited significantly better responses to ICB across different cancer types and treatment regimens. This predictive capability makes the Bonavita scan tool a valuable asset for optimizing patient selection for immunotherapy.
Conclusion: Personalizing Cancer Treatment with the Bonavita Scan Tool
The Bonavita scan tool, by deciphering the complex inflammatory landscape of tumors, provides a powerful new approach for predicting immunotherapy outcomes. Its ability to integrate key inflammatory factors and immune cell activity into a single, clinically relevant score holds immense potential for personalizing cancer treatment and improving patient outcomes. Further research and clinical validation will refine its application and solidify its place as a crucial tool in the fight against cancer.